7A: Wound Healing
Types of wounds
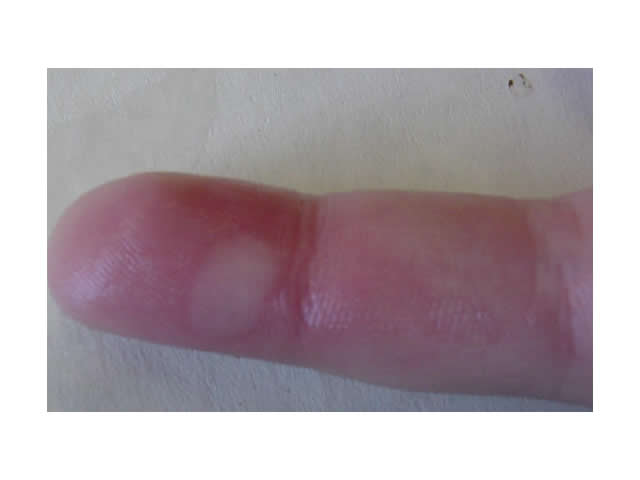
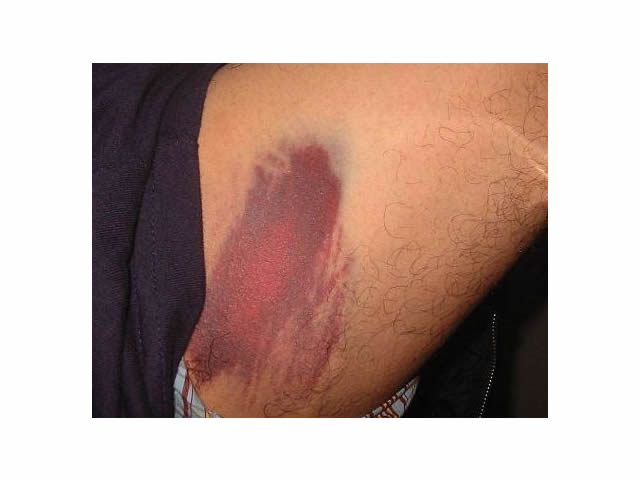
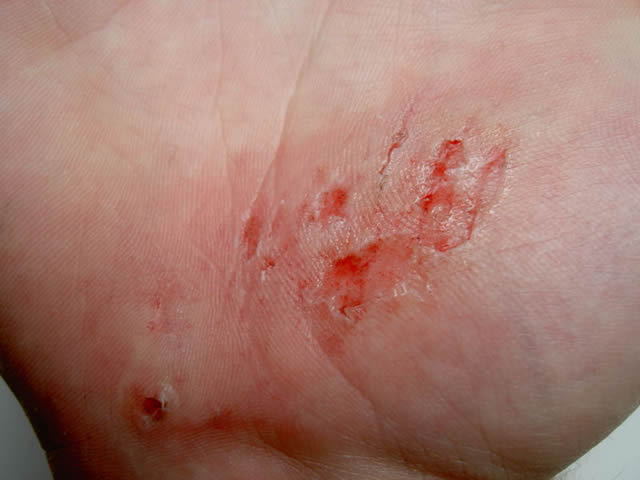
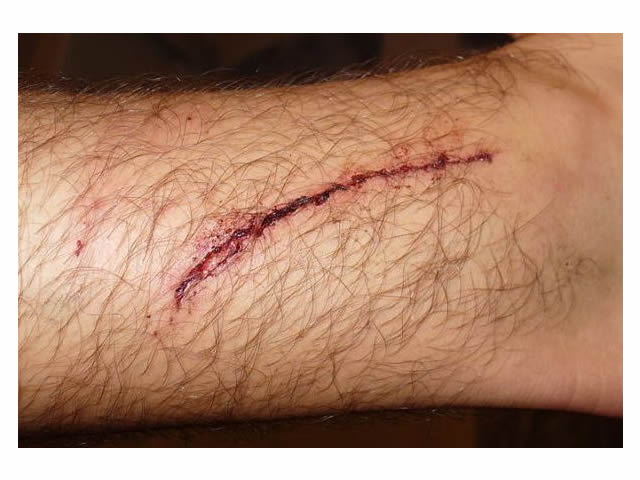
A wound can be defined as an injury to the skin or underlying structures that may or may not result in a loss of skin integrity. This means that the physiological function of the tissue is impaired. Common wound types are listed in this table:
| Wound type | Examples |
| Traumatic wounds |
|
| Thermal injuries |
|
| Wounds inadvertently caused by a clinician, medical treatment or diagnostic procedure (iatrogenic injury) |
|
Wounds can also be classified as follows:
| Classification | Explanation | Examples |
| Acute | Acute wounds heal fairly quickly (usually within 14 days), without complications and with limited interventions required. |
|
| Chronic | A chronic wound is one that has failed to heal within four to six weeks despite appropriate treatment. |
|
Top of page
Wound healing phases
Wound healing progresses through the phases as described in this table:
| Phase | Explanation |
| Vascular response (haemostasis) | This phase involves initial bleeding, which should stop within 10 minutes. |
| Inflammation |
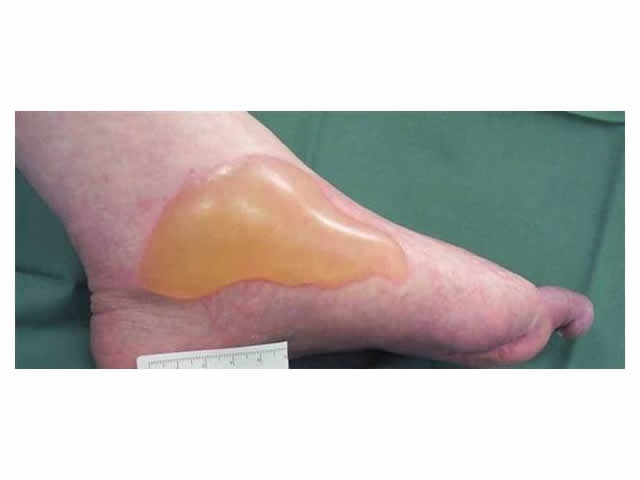
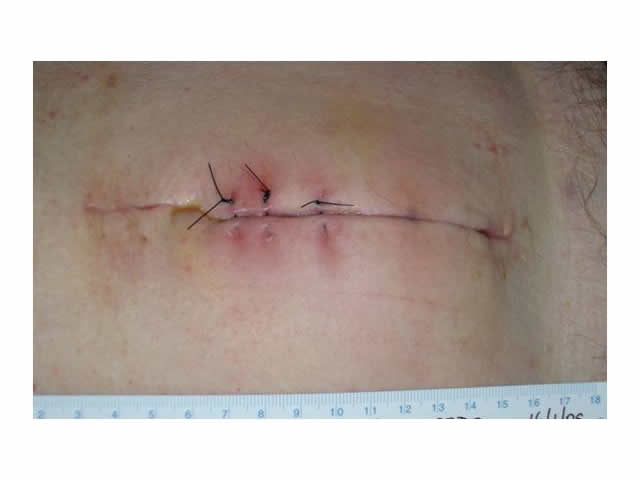
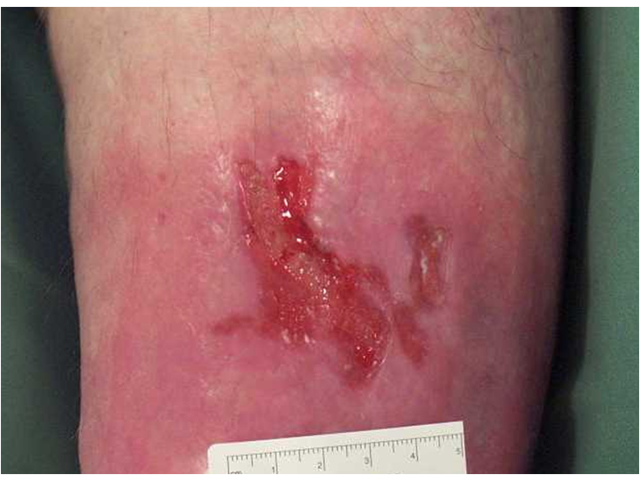
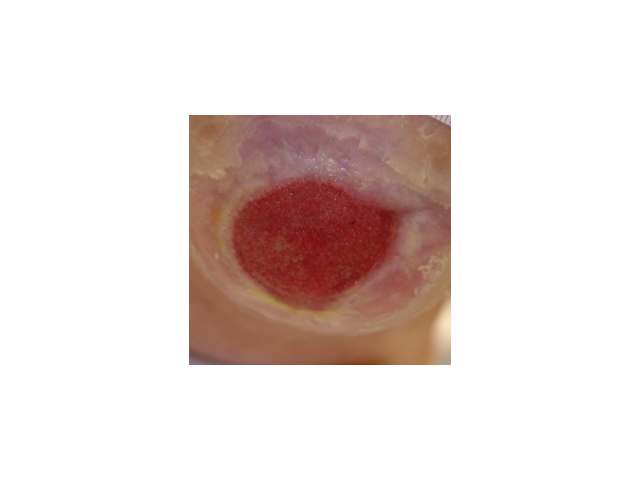
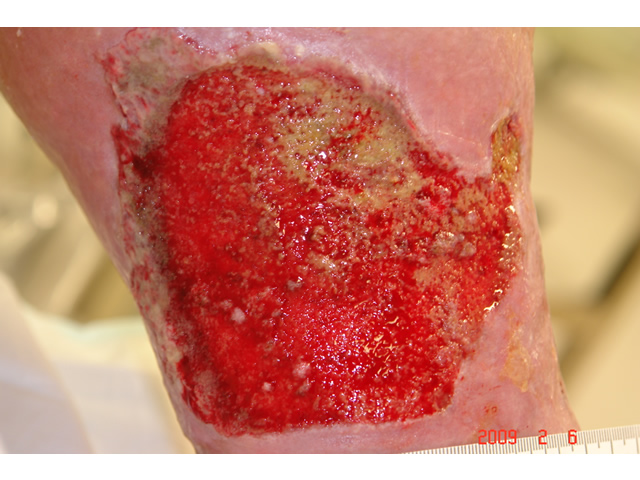
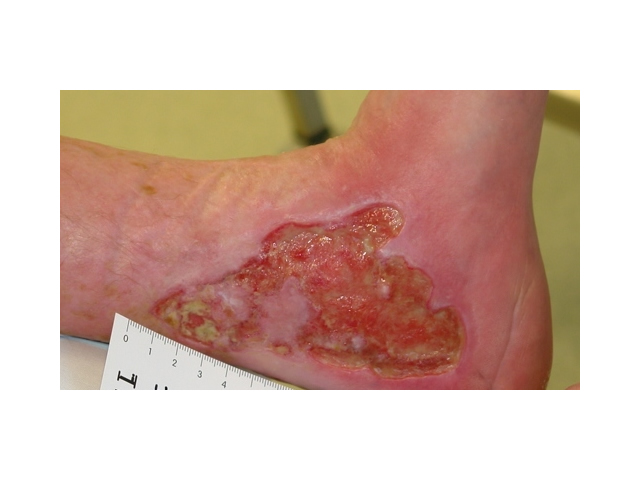
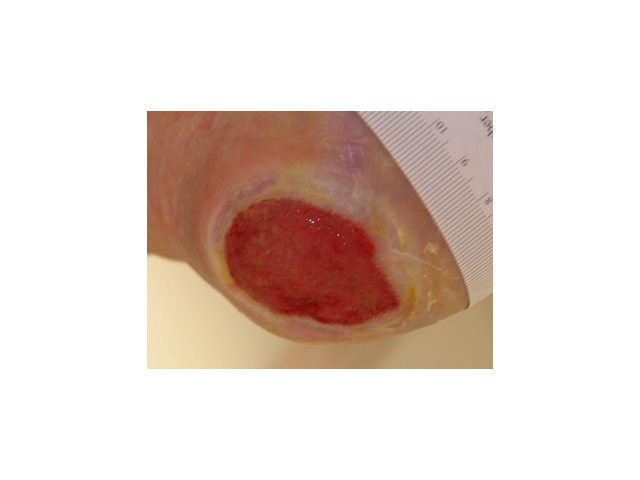
This phase lasts for around three days and is a normal process of wound healing. Signs include redness, heat, swelling, pain and functional disturbance. IMAGE - M7 07 Inflammation |
| Proliferation (new tissue growth) |
This phase lasts for around 28 days. During this phase, the wound bed tissue experiences these states:
|
| Maturation (regaining normal function) |
This is the final phase of wound healing and describes the process of the healed tissue regaining its previous levels of functional ability. This phase can last for longer than a year. Full return of strength in that tissue is never quite achieved. Complications such as contractures or excessive scar formation may occur during this phase. |
Top of page
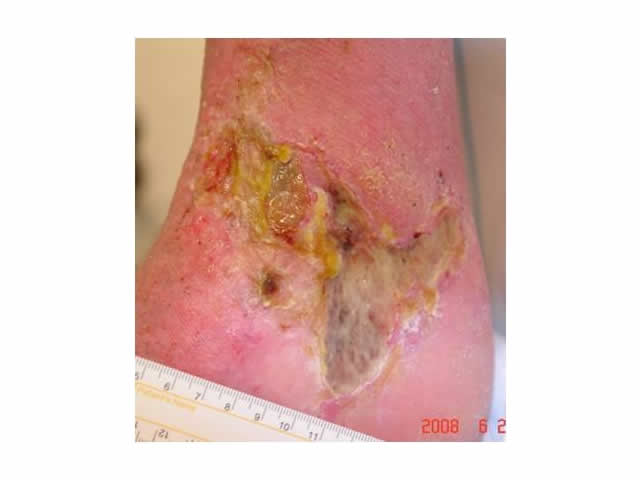
Healthy and unhealthy wounds
The following signs and symptoms provide an indication of whether a wound is healing normally or if it is remaining stagnant or deteriorating.
| Wound status | Signs and symptoms |
| Healthy |
|
| Unhealthy |
|
Top of page
Factors influencing wound healing
Being able to recognise factors that can impact on the wound healing process is essential so that you can take steps to either remove the factors slowing down the wound healing process or, if possible, minimise their impact. Some factors that may impact on the wound healing process include the following:
| Factor | Explanation |
| Health of the client | Illnesses such as renal failure, heart failure, a cerebral vascular accident and diabetes increase a person’s risk of suffering impaired wound healing because of the way these diseases affect all body systems. |
| Nutrition and hydration | Poor nutrition and hydration will slow down the wound healing process because the body will not have enough nutrients to promote wound healing. A wound increases the body’s need for nutrients, protein and energy.
Clients need to drink at least 6 to 8 glasses of fluid per day because a lack of fluids impairs the blood flow which reduces oxygen and nutrients needed in the tissue to promote wound repair. Dry skin is less elastic and more likely to breakdown. Sources of fluid include water, juice, milk, jelly, ice-cream, yoghurt, soup, tea and coffee. |
| Age | Blood flow decreases with age and the older a person is the more likely they are to have problems with their skin. Refer to Module 1 to review your understanding of the skin changes associated with ageing. |
| Medications | Some medications that make the blood less likely to clot (e.g. anticoagulants) or steroids (e.g. taken for conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis) make the skin thinner and more likely to tear. |
| Psychological state | There is a link between high levels of stress and impaired wound healing. |
| Decreased blood supply | Hardened, narrowed or blocked arteries reduce blood supply to the skin. This slows down wound healing because blood carries nutrients and oxygen. |
| Infection | The presence of a wound infection slows down healing. |
| Pressure, friction, shear | Dry skin is more likely to tear due to friction, shearing or pressure. |
| Temperature | Wounds need a stable temperature to promote the healing process. |
| Loss of sensation | Decreased sensation, loss of consciousness, an injury to the central nervous system, a cerebrovascular accident, major surgery, spinal cord injury or medications such as steroids or anticoagulants, increase the risk of skin damage. This is because the client may not be aware that an injury to the skin has occurred. |
| Smoking | Cigarette smoking is a well known risk factor for impaired wound healing because it leads to hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis) and ischaemic heart disease. |
Top of page